Liver Flukes In Stool
Author : Katrina Dare / Post on 2020-11-04

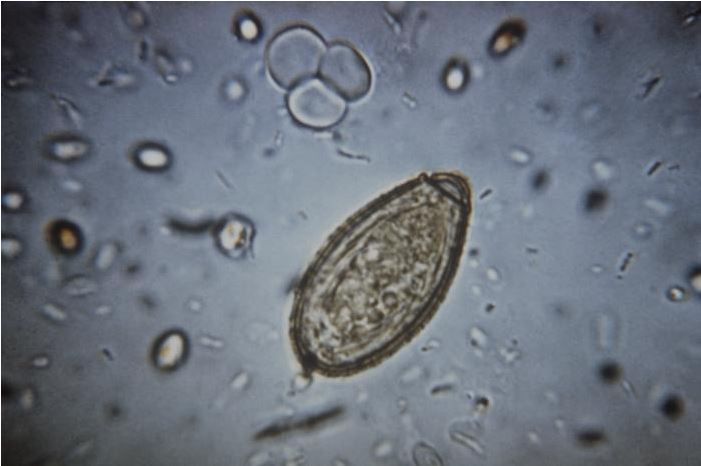
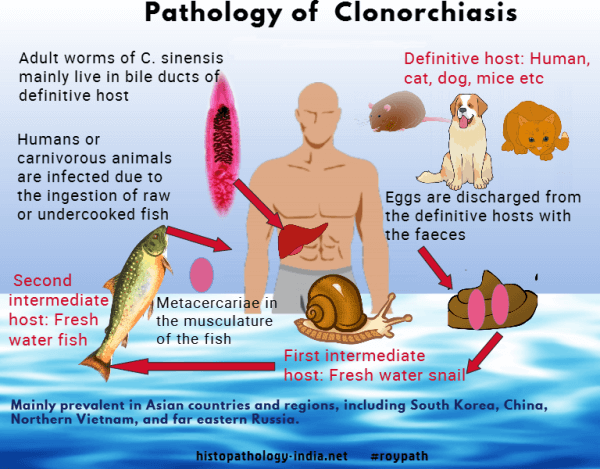
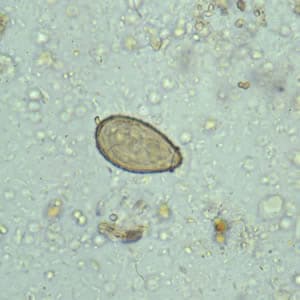
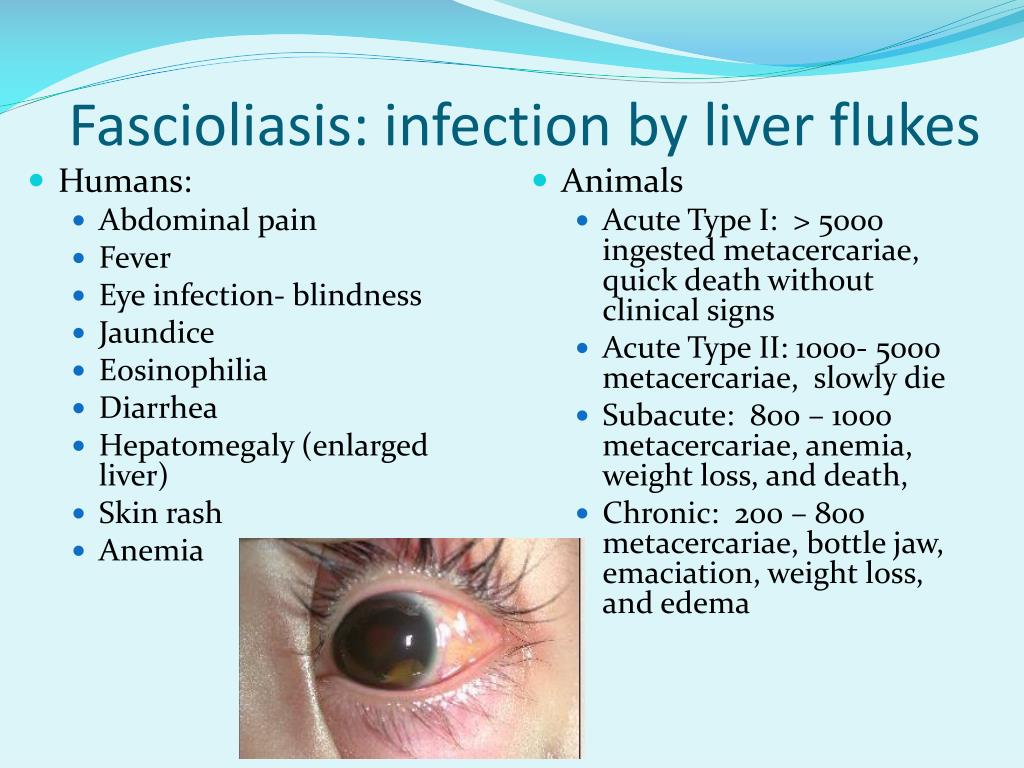
Liver Flukes In Stool. The irritation and scarring caused by liver fluke infection can your health care provider can arrange for examination of your stool to check for ongoing liver fluke infection. Your risk of infection increases if you travel to parts of the world where this may leave you wondering if your liver fluke infection has cleared. Clonorchis is a liver fluke parasite that humans can get by eating raw or undercooked fish, crabs, or crayfish from areas where the parasite is found. Each one is unique for. Flukes that cause schistosomiasis, paragonimiasis, fascioliasis, clonorchiasis, and opisthorchiasis are included in the world health organization (who) list of neglected tropical diseases (ntd) to which interventions for poor and marginalized populations are prioritized given the significant health burden. The eggs then embryonate in. Clonorchis sinensis, various opisthorchis species (viverrini, felineus) and fasciola species (hepatica. Clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, and the north american liver fluke, metorchis conjunctus, will be reviewed here. Fasciola hepatica is identified from eggs in a stool sample. Liver flukes are a group of about fifteen different species of parasites that share a number of characteristics during their life cycle and result in a similar etiology when they infect humans. The only sure way to tell is to revisit your doctor, who can test your stool to see. Conventional ova and parasite stool test. Liver flukes are an important cause of acute and chronic disease in grazing sheep and cattle.
In liver fluke infection, ultrasound and abdominal ct scan may be useful to assess the presence of complications requiring surgical intervention or lung flukes. Eia and western blotting are highly sensitive and specific and may be. Detection of eggs in sputum and stool may be difficult and insensitive. Infected snails release immature flukes (cercariae), which form cysts. Liver flukes infect the liver, gallbladder, and bile duct in humans.

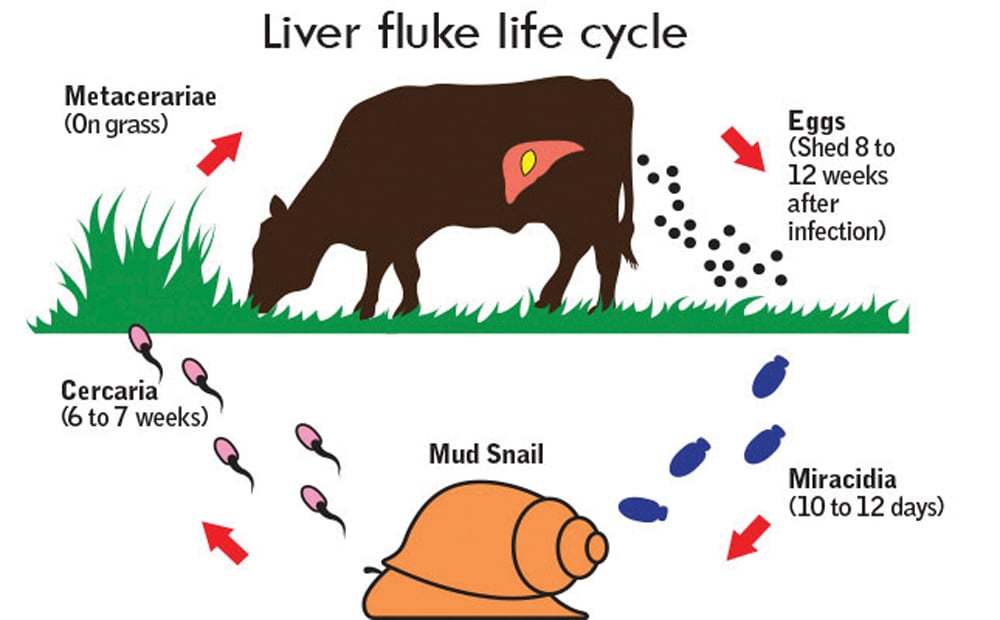
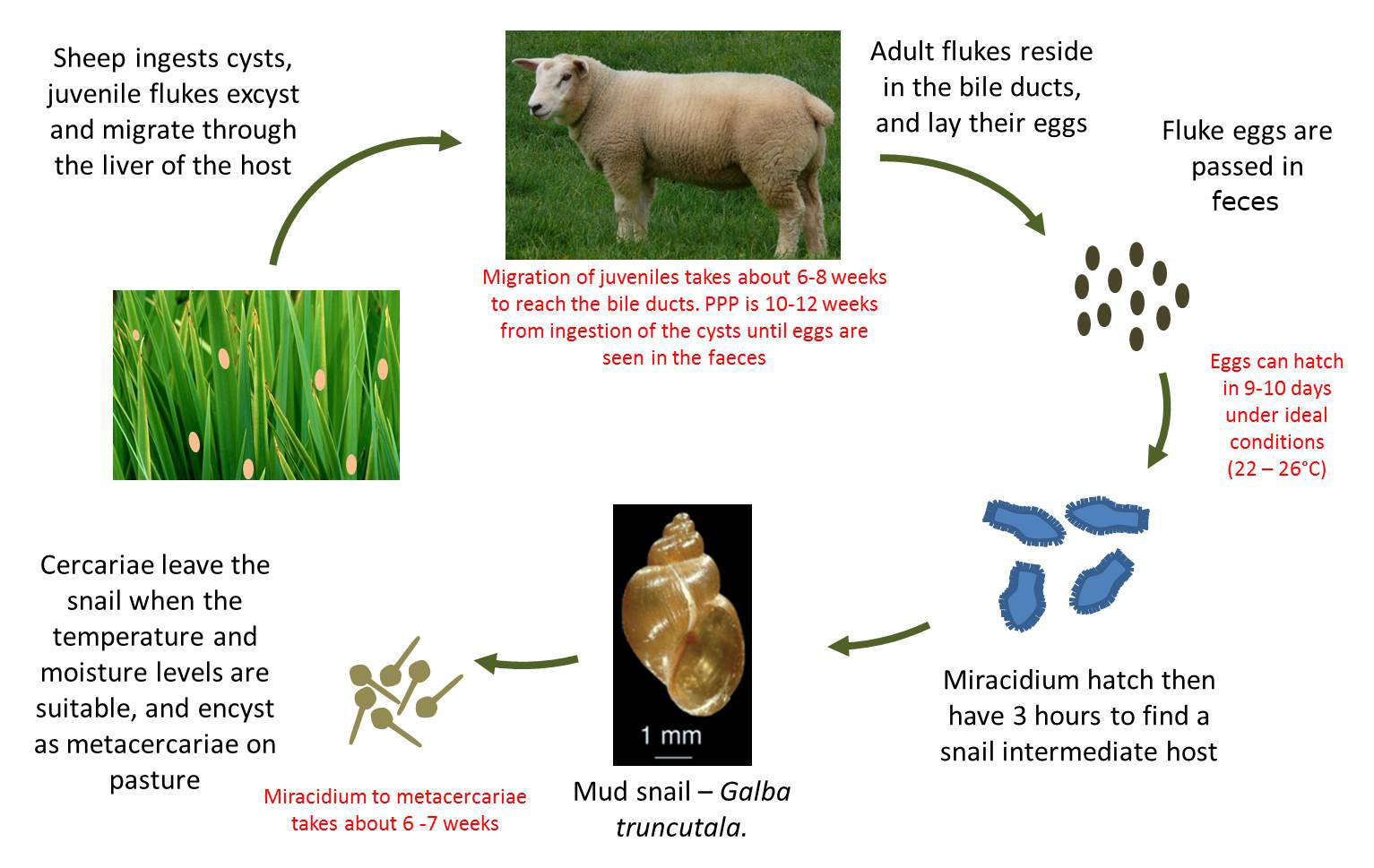
Clonorchis sinensis, various opisthorchis species (viverrini, felineus) and fasciola species (hepatica. The veterinarian may also take a stool sample in order to look for. This can yield a false negative for the. Its final hosts are sheep, goats, cattle and other domestic and wild mammals, including horses, dogs, cats and humans. Fasciola hepatica is identified from eggs in a stool sample. The eggs then embryonate in. They are principally parasites of the liver of various mammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also in bile ducts, gallbladder. The liver flukes are several species of trematodes that cause disease by interfering with the bile duct. Clonorchis sinensis, various opisthorchis species (viverrini, felineus) and fasciola species (hepatica. Usually, the eggs of the fluke are discharged in the stool of an infected animal. Flukes that cause schistosomiasis, paragonimiasis, fascioliasis, clonorchiasis, and opisthorchiasis are included in the world health organization (who) list of neglected tropical diseases (ntd) to which interventions for poor and marginalized populations are prioritized given the significant health burden. Clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, and the north american liver fluke, metorchis conjunctus, will be reviewed here. Fascioliasis is caused by fasciola hepatica and fasciola gigantica in contaminated raw or undercooked aquatic plants (e.g., watercress). These samples will be sent to the lab in order to look for the presence of the fluke. Eggs in stool, ultrasound of bile ducts, eosinophilia/serology ests can detect flukes 2 weeks after infection. Clonorchis is a liver fluke parasite that humans can get by eating raw or undercooked fish, crabs, or crayfish from areas where the parasite is found. The life cycle of flukes eggs are passed in stool. Caused by a flat worm called fasciola hepatica.

Liver fluke infections aren't common in the united states, but they do occur. Your risk of infection increases if you travel to parts of the world where this may leave you wondering if your liver fluke infection has cleared. Infected snails release immature flukes (cercariae), which form cysts.
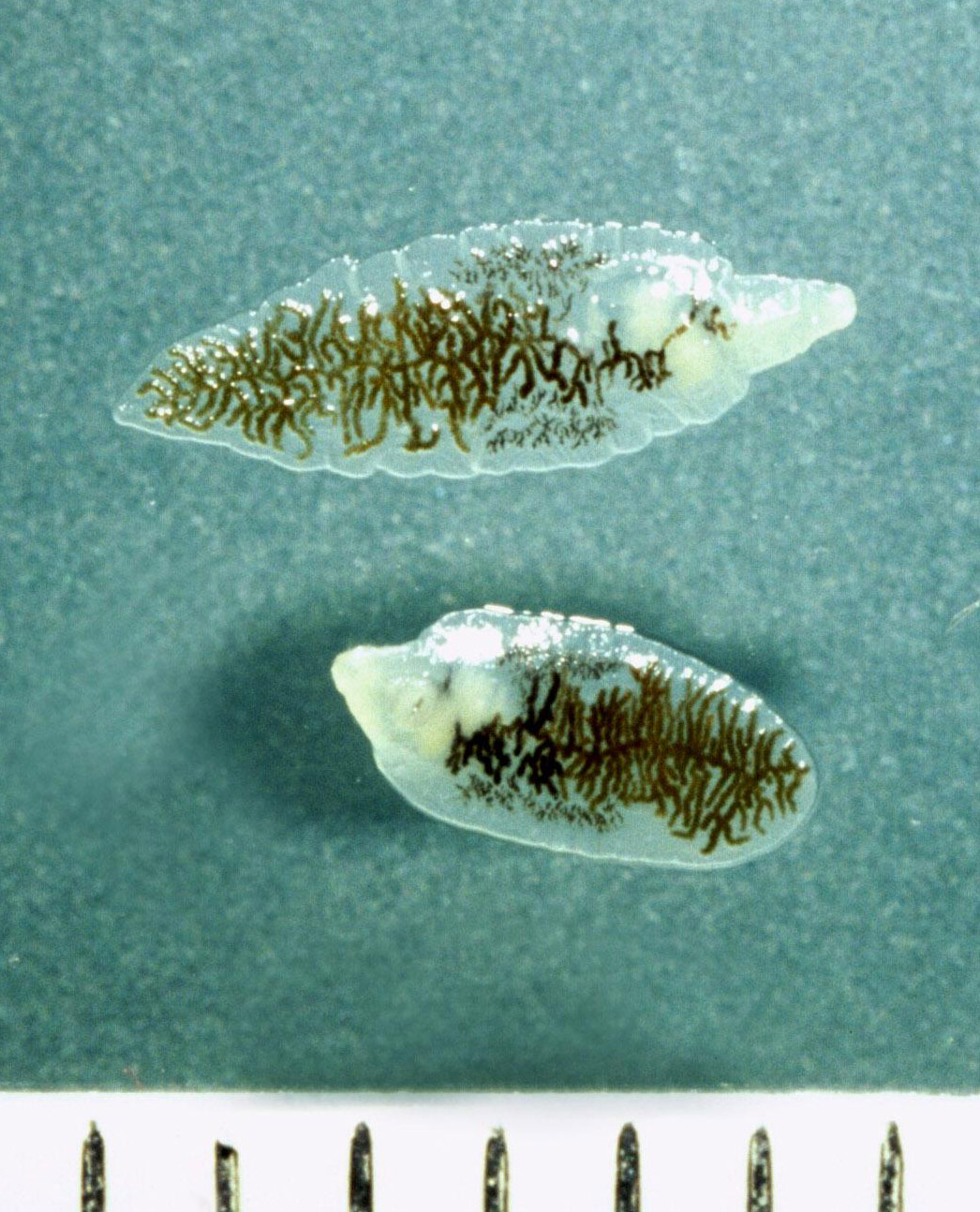
There are three major types of liver flukes pathogenic for humans: Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode (fluke or flatworm, a type of helminth) of the class trematoda, phylum platyhelminthes. In water, the eggs release larvae, which penetrate snails. The only sure way to tell is to revisit your doctor, who can test your stool to see. The life cycle of flukes eggs are passed in stool. Clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, and the north american liver fluke, metorchis conjunctus, will be reviewed here. If the metacercariae are ingested by. In particular, although they can be in several places in the body during the parasite's life cycle. Detection of eggs in sputum and stool may be difficult and insensitive. It is important to understand the life cycle of the liver fluke when looking at the spread of these worms. See your doctor, especially if you've traveled to asia (flukes are endemic there). Fasciola hepatica is identified from eggs in a stool sample. Clonorchis sinensis, various opisthorchis species (viverrini, felineus) and fasciola species (hepatica. The condition can cause severe diseases in a range of animals liver flukes cannot be spread from person to person. These samples will be sent to the lab in order to look for the presence of the fluke. Once eaten, the liver flukes grow to adulthood inside the human biliary duct system. Eggs in stool, ultrasound of bile ducts, eosinophilia/serology ests can detect flukes 2 weeks after infection. Fasciola hepatica (the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke), which causes fascioliasis and typically infects sheep and cattle. In liver fluke infection, ultrasound and abdominal ct scan may be useful to assess the presence of complications requiring surgical intervention or lung flukes.
The liver flukes are several species of trematodes that cause disease by interfering with the bile duct. There are three major types of liver flukes pathogenic for humans: In the continental u.s., fasciola hepatica infections are primarily seen in there are three common species of flukes in ruminants of the continental united states: The eggs then embryonate in. The condition can cause severe diseases in a range of animals liver flukes cannot be spread from person to person. Eggs in stool, ultrasound of bile ducts, eosinophilia/serology ests can detect flukes 2 weeks after infection. See your doctor, especially if you've traveled to asia (flukes are endemic there). The veterinarian may also take a stool sample in order to look for. Fasciola hepatica, fascioloides magna, and. Once eaten, the liver flukes grow to adulthood inside the human biliary duct system. It is known as the common liver fluke and causes a disease called fascioliasis. Liver fluke infections aren't common in the united states, but they do occur. Endemic to certain parts of asia. Consumption of raw/undercooked freshwater fish. The eggs are very similar to those of fasciolopsis buski. If the infection occurred years ago, the test may. The liver fluke is a parasite found in the bile ducts and the liver. Conventional ova and parasite stool test. Liver flukes are common in certain parts of the world.
Leave a Comment:
Search
Categories
Popular Post
Liver Flukes In Stool
Liver fluke in sheep also known as:
Liver Flukes In Stool
Liver flukes are an important cause of acute and chronic disease in grazing sheep and cattle.
Liver Flukes In Stool
Liver fluke is a collective name of a polyphyletic group of parasitic trematodes under the phylum platyhelminthes.
Liver Flukes In Stool
Diagnosis of liver fluke is not simple.
Liver Flukes In Stool
Infected snails release immature flukes (cercariae), which form cysts.















1.jpg)